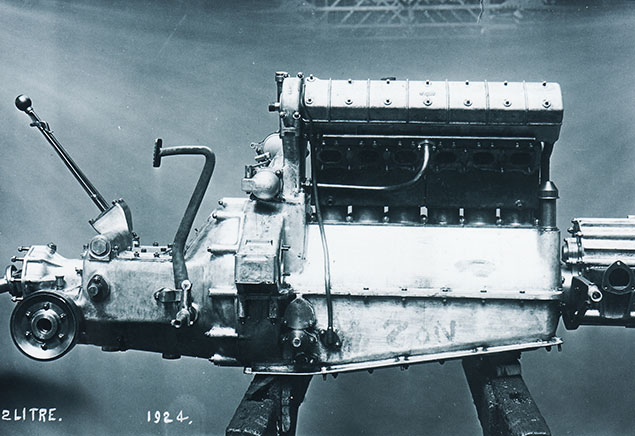
2-litre (67x94mm, 1,988cc) six-cylinder supercharged. Mounted on the chassis frame. Two blocks of three; each
cylinder barrel is a separate forging complete with non-detachable head welded onto a common baseplate; ports and water jacket welded around adding rigidity. Two valves per cylinder inclined at 96 degrees operated by twin
camshafts driven by spur gear train from rear of crankshaft; actuating pivoted fingers and running in roller bearings. Inlet valves 30% larger than Exhaust valves. Main and big end bearings are all split-cage roller bearings. One piece crankshaft running in eight main bearings. Domed and recessed aluminum Pistons. Machined steel connecting rods, each housing split cage roller bearing for the big end.
Roots blower driven off the front end of the crankshaft placed between the Solex carburetors (48 choke Barrel
throttle) and induction manifold thereby gaining 23bhp or 25% power increase; output throughout the range was
also improved to give improved acceleration.
Mechanical petrol pump driven off the inlet camshaft was fitted for the 1925 Grand Prix since riding mechanics
were no longer carried.
In 1924 the engine developed 138bhp at 5,000rpm (146.5bhp at maximum rev) with compression 6.2 and
supercharger boost 6psi. Boost was raised to 9.5psi in 1925 with 60/40 mixture of petrol/benzole resulting in
150bhp. By 1928 and running on E2 (50% ethyl alcohol, 25% petrol, 25% benzole) it developed 170bhp at 5,500.